[新しいコレクション] define gravitational constant g class 9 194499-Define gravitational constant g class 9
Square the distance between the two objects (638 x 10 6) 2 = 407 x 10 13; · Multiply the product of m 1 and m 2 by the gravitational constant G (406 x 10 26) x (667 x 1011) = 2708 x 10 16; · This example also demonstrates a problem with Enum in the surface_gravity () property method, a constant G is defined which would normally be defined at class level – but attempting to do so inside an Enum would simply add it as one of the members of the enum, so instead it's been defined inside the method

Universal Gravitational Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Define gravitational constant g class 9
Define gravitational constant g class 9-Acceleration due to gravity ' g ' for a body of mass ' m ' on earth's surface is proportional to (Radius of earth= R , mass of earth= M 59k 11k 140 If M is the mass of the earth and R its radius, then ratio of the gravitational acceleration and the gravitational constant isG is the universal gravitational constant, G = 6674 x 1011 m3 kg1 s2 M is the mass of the body measured using kg R is the mass body radius measured by m g is the acceleration due to the gravity determined by m / s2 The mass of the moon is 735 × 1022Kg Thus, the value of g on the moon is g=1625m/s2




Define Gravitational Constant G
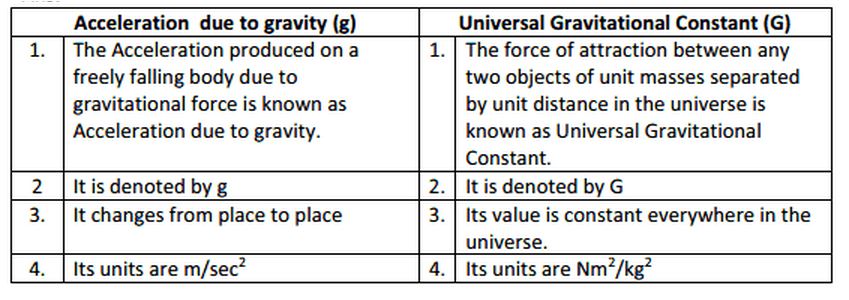
Medium View solution State SI unit & dimension of universal gravitational constant · Universal Gravitation Constant ( G ) The acceleration gained by a body when it is under is in free fall due to the gravitational force The force of attraction between two bodies with unit mass which are in unit distance at any part of this universe It will change from place to place Constant at any place in the universe Value of g=98 m/s 2The acceleration on an object due to the gravity of any massive body is represented by g (small g) The force of attraction between any two unit masses separated by unit distance is called universal gravitational constant denoted by G (capital G) The relation between G and g is not proportional That means they are independent entities
G is the gravitational field strength in newtons per kilogram, N/kg h is the change in height in metres, m For example, a book with a mass of 025 kg is lifted 2 m onto a book shelfEnum Types An enum type is a special data type that enables for a variable to be a set of predefined constants The variable must be equal to one of the values that have been predefined for it Common examples include compass directions (values of NORTH, SOUTH, EAST, and WEST) and the days of the week Because they are constants, the names ofVARYING G AND Λ Uttam Kumar Dwivedi* Abstract I have discussed about aLRS Bianchi type I cosmological model filled with stiff fluid, variable gravitational constant and cosmological constants The cosmological models are obtainedby assuming the cosmological term inversely proportional to scale factor
Dictionary of physical constants, of the format physical_constants name = (value, unit, uncertainty) Available constants alpha particle mass e27 kg alpha particle mass energy equivalent e10 J alpha particle mass energy equivalent in MeV MeV/12/11 · • G is a constant throughout space and time, but g is a variable quantity • Gravitational acceleration depends on the universal gravitational constant, but the universal gravitational constant is independent of the gravitational acceleration • The basic units of g are ms2, whereas the units of G are m 3 s2 kg1 · 1It is define as the constant acceleration produced in a body when it falls freely under the effect of gravity 2 its value changes from place to palce 3 it is a vector quantity 4




The Search For Newton S Constant Physics Today Vol 67 No 7




Define Gravitational Constant G
Chapter 10 Science Class 9 will also define the gravitational constant and gravitational acceleration Eventually, you will proceed to understand how the equations of motion can be related to this chapter With the help of these equations, you can calculate the velocity of a freely falling object easily Eventually, you will reach the exercise/05/ · Thus, the value of acceleration due to gravity of the earth, g = 98 m/s 2 Difference between Gravitation Constant (G) and Gravitational Acceleration (g) · The gravitational constant is the proportionality constant used in Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation, and is commonly denoted by G This is different from g, which denotes the acceleration due to gravity In most texts, we see it expressed as G = 6673×10 –11 N m 2 kg –2 What is value of G?
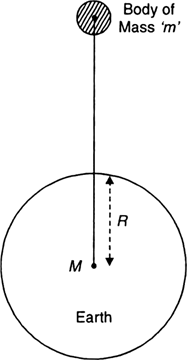



Define Acceleration Due To Gravity Deduce An Expression For It In Terms Of Mass Of The Earth M And Universal Gravitational Constant G




Derive Expression For Force Of Attraction Between Two Bodies And Then Define Gravitational Constant Cbse Class 9 Science Learn Cbse Forum
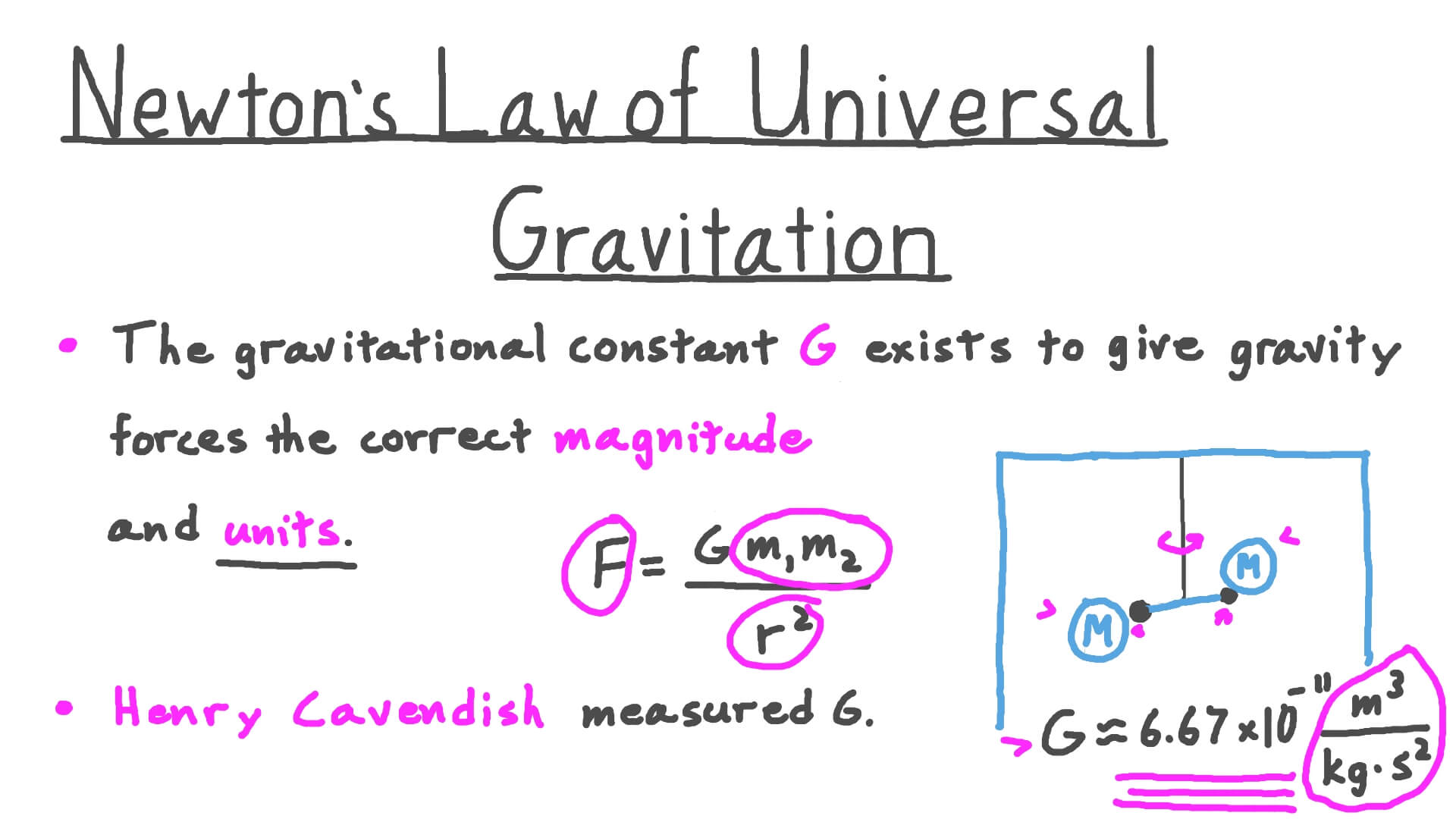
· G = F Thus, the gravitational constant G is numerically equal to the force of gravitation which exists between two bodies of unit masses kept at a unit distance from each other Question 2 Define acceleration due to gravity Derive an expression for acceleration due to gravity in terms of mass of the earth (M) and universal gravitational constant (G) · Gravitational force = (G * m1 * m2) / (d2) Gravitational force = (G * m1 * m2) / (d 2) where G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects for which you are calculating the force, and d is the distance between the centers of gravity of the two masses G has the value of 667 x 10E8 dyne * cm 2 /gm 2 So if you · admin March 3, 0 12,5 1 minute read The basic difference between g and G is that 'g' is the Gravitational acceleration while 'G ' is the Gravitational constant The value of g changes with altitude while the value of G remains constant Gravitational acceleration is the vector quantity and gravitational constant is the scalar




What Is The Value Of Gravitational Constant Value Of Capital G



Explain Universal Gravitational Constant Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
· 1 Introduction The existence of scalar fields whose vacuum expectation values determine the physical constants is generically predicted by the recent attempts toward unifying all elementary forces in nature based on string theory In this context, scalar–tensor theories of gravity are a natural alternative to the Einstein gravity since they arise from the lowenergy limitThis quantity is sometimes referred to informally as little g (in contrast, the gravitational constant G is referred to as big G) The precise strength of Earth's gravity varies depending on location The nominal "average" value at Earth's surface, known as standard gravity is, by definition, m/s 2 · G is a constant and is known as Gravitational constant Value of G = 667×10 11 Nm 2 /kg 2 G is called universal gravitational constant → If unit of F is in Newton, m is in kg, d is in metre, then unit of G can be calculated as




Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Wikipedia
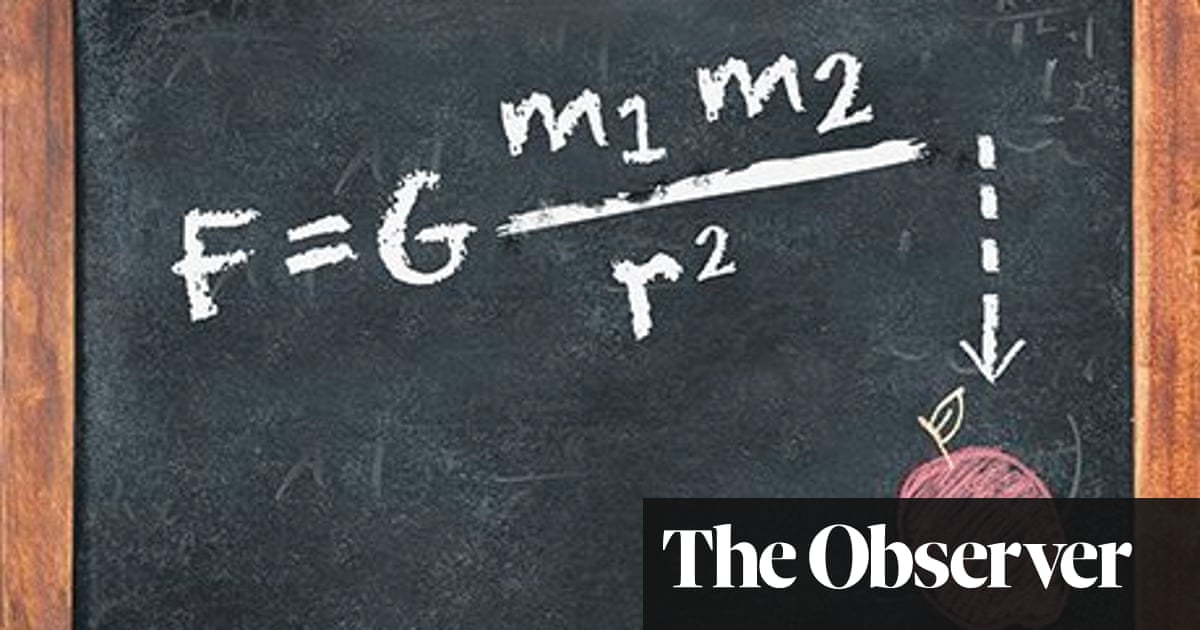



Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation Isaac Newton The Guardian
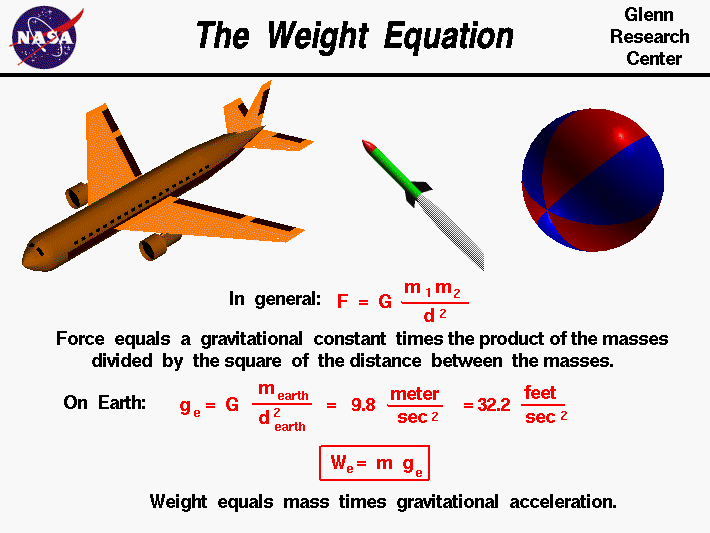
1 Weight of the body is the force with which it is attracted towards the earth (W = m x g) 2 Its SI unit is kg 2 Its SI unit is Newton 3 It remains constant everywhere and it cannot be zero 3 Its value changes from place to place and it can be zero 4 It can be measured by beambalance 4 It can be measured by spring balance 5Class 9 Science Chapter 22 16 Qs Related questions View solution View solution View solution Write the S I unit of Gravitational constant Medium View solution Define Universal gravitational constant G What is the dimensional formula G? · Expert Answer The acceleration produced in freely falling body due to gravitational force is called acceleration due to gravity Acceleration due to gravity is represented by letter 'g' Value of g is 98 m/s 2




C H A P T E R 4 Forces And Newton S Laws Of Motion Ppt Video Online Download




Pdf Measurements Of Newton S Gravitational Constant And The Length Of Day
· Abstract The Newtonian gravitational constant G, which is one of the most important fundamental physical constants in nature, plays a significant role in the fields of theoretical physics, geophysics, astrophysics and astronomyAlthough G was the first physical constant to be introduced in the history of science, it is considered to be one of the most · The gravitational constant is the proportionality constant used in Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation, and is commonly denoted by G This is different from g, which denotes the acceleration due to gravity G = 6673×1011 N m^2 kg^2 g = 98 m/s^2 · G is the gravitational constant The gravitational force between two bodies of masses m1 & m2, separated by a distance d is given by The value of G is 6674 X 10^ (11) Nm^2/kg^2 This is a universal constant g is the the acceleration due to gravity This varies, even on the earth from place to place




Gravitation




Define Gravitational Constant G
The gravitational constant is the proportionality constant used in Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation, and is commonly denoted by G This is different from g, which denotes the acceleration due to gravity In most texts, we see it expressed as G = 6673×10 –11 N m 2 kg –2 · In this post, we will list down and derive the formula of Acceleration due to gravity on the earth's surfaceIn other words, we will derive the formula or equation of g on the earth's surface The 2 formulas we will derve for g (Acceleration due to gravity on the earth's surface) are g = GM / R 2 and g = (4/3) π R ρ G So let's start with the step by step derivation processConstant (04), g is the gravitational constant, and H, is the vertical heat flux The difficult measurement to obtain is, of course, H, The correlation developed by Pasquill and Smith (1971) for flow over short grass, with z, = 001 m is given in Table AS TABLE AS PasquillGifford Stability Class Correlated with MoninObukov Length



Weight Equation




Define Universal Gravitational Constant Give Its Value With Si Un
Divide the product of G x m 1 x m 2 by the distance squared to find the force of gravity in Newtons (N) 2708 x 10 16 /407 x 10 13 = 665 N; · (i) Universal gravitational constant is the constant 'G' appearing in Newton's law of gravitation F=GMm/r 2 where, F is the force between two masses m and M at a distance r apart The numerical value of G is equal to 6673×1011 Nm 2 kg2 The value of G was found out by Henry Covendish by using a sensitive balanceGravitational constant is equal to the force of attraction that exists between two bodies of masses separated by distance one meter If we take this concept in notice that all bodies attract each other, then why do we always see all objects moving towards earth, why not movement in the earth towards the objects This is because as we know




What Is Gravity Live Science



Gravitational Field
Gravitational field strength (g) is measured in newtons per kilogram (N/kg) Example Calculate the energy transferred to the gravity store when a woman of mass 60 kg climbs 4 rungs up a ladderWhat is the SI unit of G and g?In the first equation above, g is referred to as the acceleration of gravity Its value is 98 m/s2 on Earth That is to say, the acceleration of gravity on the surface of the earth at sea level is 98 m/s 2 When discussing the acceleration of gravity, it was mentioned that the




Q 1 Define Gravitation How Is It Different From Gravity E Ctlt




Gravitational Constant Ewt
· G Gravitational Constant is an empirical physical constant that is involved in the calculation of gravitational effects in Newton's Law of Universal Constant Constant at any point in this universe G = ×1011Nm2/kg2 L 3 M 1 T 2Noun 1 universal gravitational constant the universal constant relating force to mass and distance in Newton's law of gravitation constant of Universal gravitational constant definition of universal gravitational constant by The Free Dictionary universal class;G is the universal gravitation constant, aka Newton's constant It is approximately 6674×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2 g is the acceleration due to gravity, and is approximately 981 m⋅s−2 On the other hand, if you mean what d



Gravity Applications




Gravitational Constant Wikipedia
· The first is the acceleration due to gravity (or gravitational field strength), which is represented by g and is an average of 98 m/s^2 on Earth But then there's G
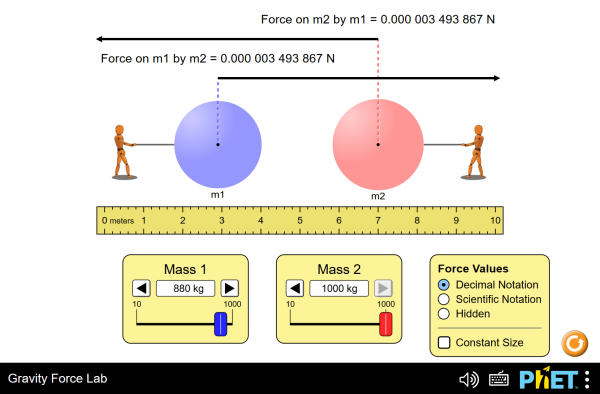



Gravity Force Lab




What Is Universal Law Of Gravitation Class 9 Gravitation Teachoo




Define Acceleration Due To Gravity Derive An Expression For Acceleration Due To Gravity In Terms Of Mass Of The Earth M And Universal Gravitational Constant G Cbse Class 9 Science




Gravitational Constant Explained Youtube



1




Introduction To Newton S Law Of Gravitation Video Khan Academy




Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation Physics




Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 3 Gravitation Free Pdf




Relation Between G And G Dewwool



What Is The Relation Between G And G Gravitation Science Class 9




Give Difference Between Universal Gravitational Constant G And Acceleration Due To Gravity G Brainly In



1



What Is Difference Between G And G Gravitation Science Class 9




Universal Gravitational Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




What Is Difference Between G And G




Lakhmir Singh Gravitation Solve Examples Class 9 Buoyancy Gravity



What Is The Gravitational Constant Universe Today



Q Tbn And9gcr8 Jzs3x7ofawjiuvhlcobzzvz5t 4pzgglmcowlxgtmql2spv Usqp Cau



Lesson Video Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Nagwa




Gravity Definition Physics Facts Britannica




What Is The Value Of Gravitational Constant Value Of Capital G



Sir Isaac Newton The Universal Law Of Gravitation




Mastering Physics Solutions Chapter 12 Gravity A Plus Topper




Swift Learning Center



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation




M 1l 3t 2 Are The Dimensions Of
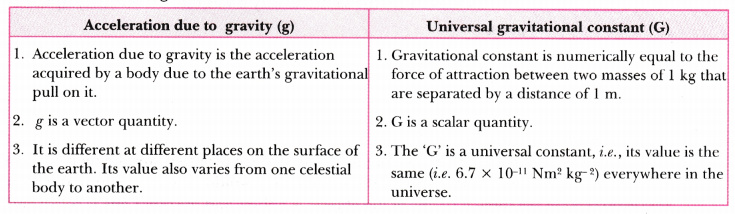



Give Three Differences Between Acceleration Due To Gravity G And Universal Gravitational Constant G Cbse Class 9 Science Learn Cbse Forum




The Si Unit Of Gravitational Constant Is Youtube



Gravitation Chapter Notes Dronstudy Com



Universal Law Of Gravitation Learn Physics Class 9 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network




What Is The Change Of Value Of G With The Depth Of Earth Explain With Derivation Physics Topperlearning Com Wzw2xw11




Calculating Acceleration Due To Gravity Formula Concept Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
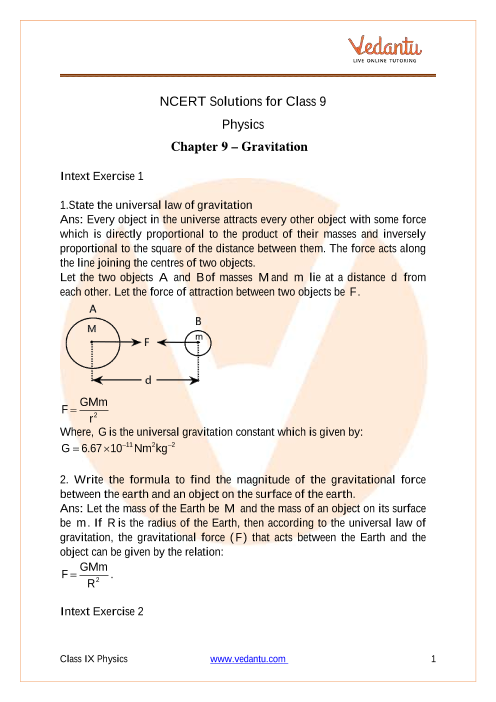



Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation Free Pdf



Gravitation Ib Physics Stuff




Universal Gravitational Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Gravitational Potential Energy




Define Acceleration Due To Gravity Deduce An Expression For It In Terms Of Mass Of The Earth M And Brainly In
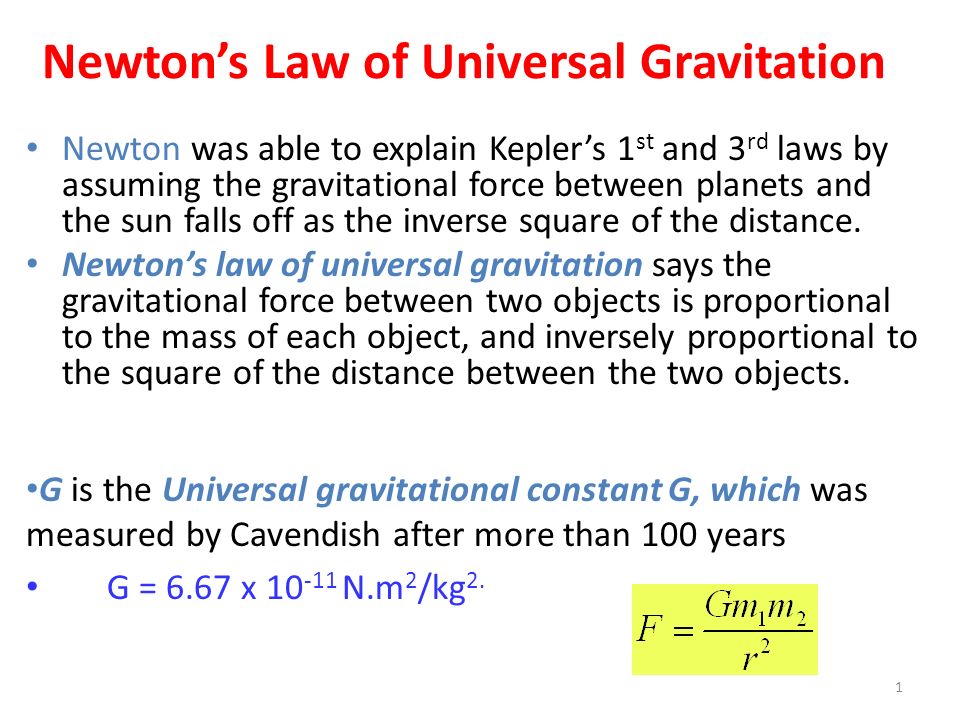



Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Newton Was Able To Explain Kepler S 1 St And 3 Rd Laws By Assuming The Gravitational Force Between Planets And The Ppt Download




Define Acceleration Due To Gravity Derive An Expression For Acceleration Due To Gravity In Terms Of Brainly In



Www Rcsdk12 Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid Dataid Filename Gravitation fr questions answers Pdf




Cbse Class 9 Science Chapter Gravitation Notes Part I
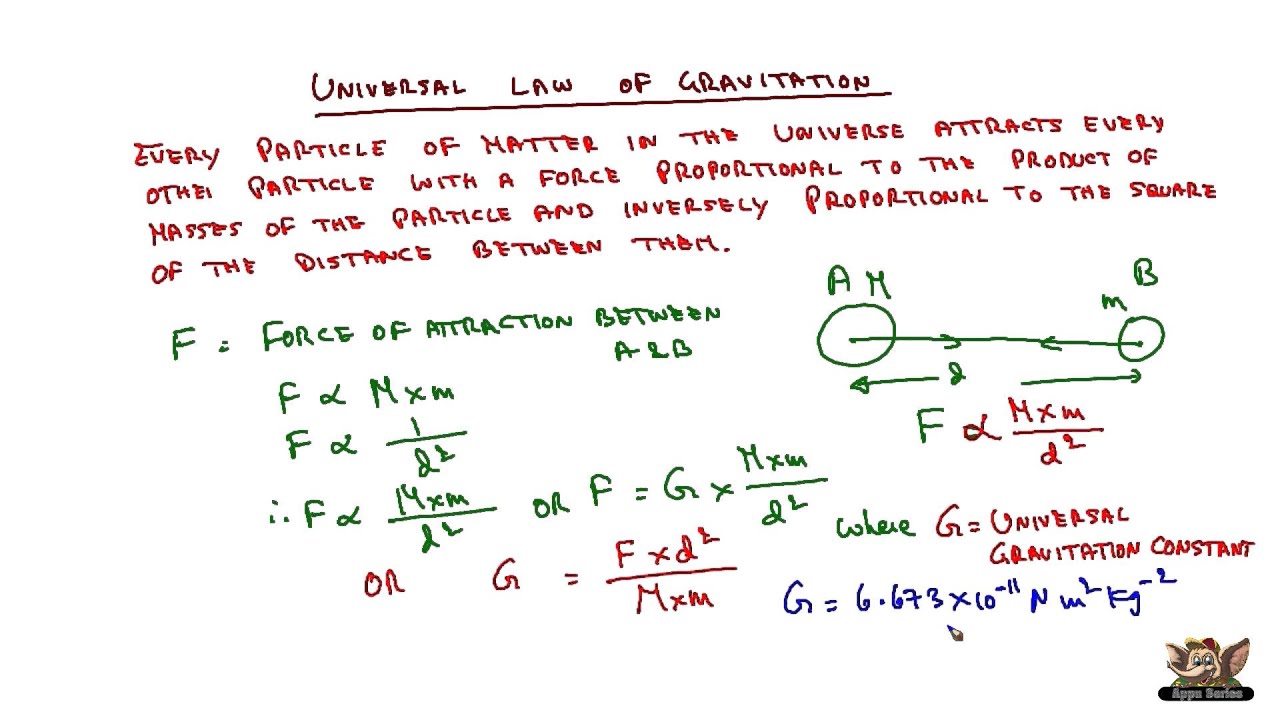



Universal Law Of Gravitation Youtube
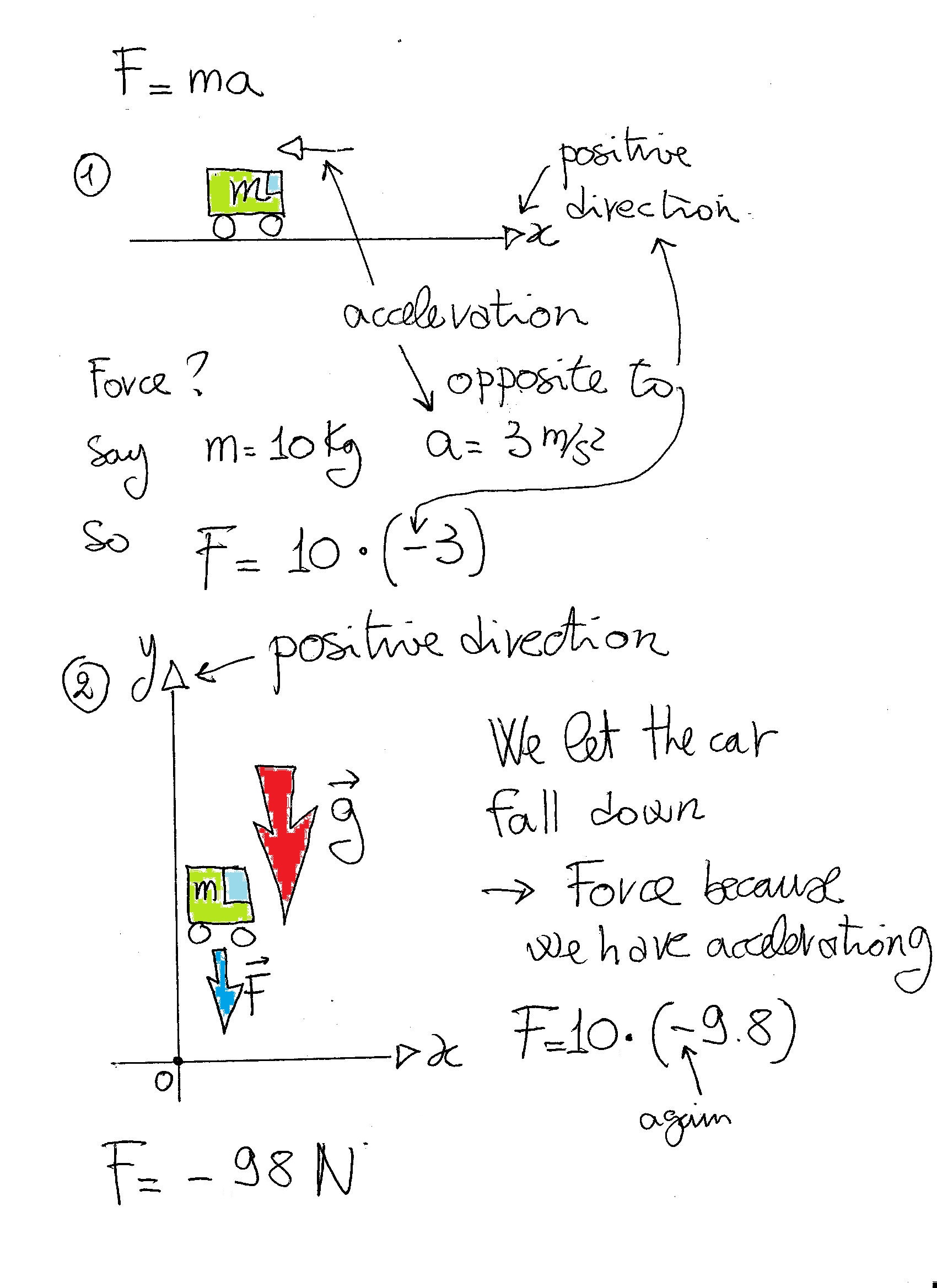



Hey I Am Too Much Confused In Taking The Sign Of G Means In Equations Like F Mg G Should Be Eq Ual To 9 8m S2 Or 9 8m S2 Please Answer With Complete Explanation



Law Of Universal Gravitation Worksheet Answers Promotiontablecovers
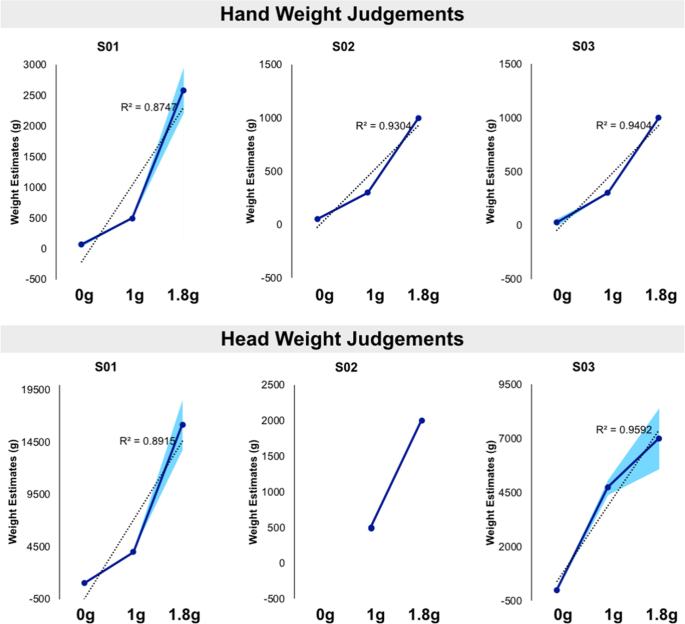



A Gravitational Contribution To Perceived Body Weight Scientific Reports




Gravity Newton S Law Of Gravity Britannica




Viewing G As The Value Of Earth S Gravitational Field Near The Surface Video Khan Academy




Pdf Newton S Gravitation Law Is Wrong
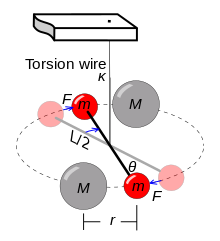



Gravitational Constant Wikipedia



What Is The Relationship Between Acceleration Due To Gravity And Mean Density In Terms Of The Gravitational Constant And The Radius Of The Earth Quora




What Is Newton S Law Of Universal Gravitation Definition Formula




The Law Of Universal Gravitation Definition Importance Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Gravitational Force Definition Equation Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
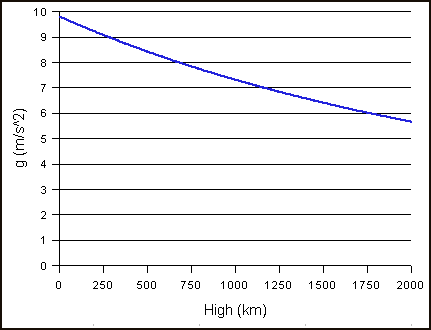



Gravity Of Earth Units Of Measurement Wiki Fandom



Ib Physics Questions On Gravitation With Answers




How To Convert Between Mass And Force In Metric And English Units



1




How To Calculate Force Of Gravity 10 Steps With Pictures




What Is Universal Law Of Gravitation Class 9 Gravitation Teachoo



The Value Of G




Gravity Definition Physics Facts Britannica




Gravitation Class 9




What Is The Relationship Between G And G Quora




Universal Gravitational Constant Gravitation And Flotation Cbse Grade 9 Physics Youtube



Define Gravitational Constan Physics Topperlearning Com Bvykdboss



What Is Difference Between G And G




What Is The Si Unit Of G And G Teachoo Extra Questions
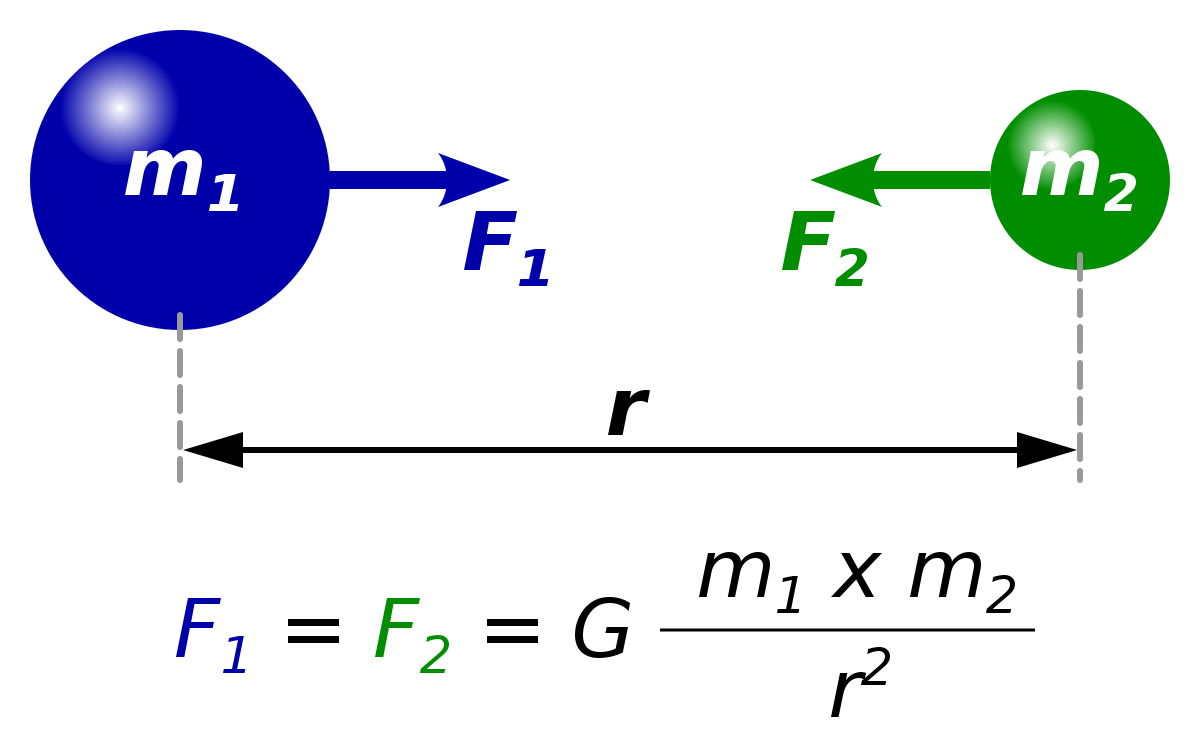



Gravitational Constant Wikipedia



What Is The Dimension Formula For A Gravitational Constant Quora



Introduction To Gravity Video Khan Academy




Cbse Class 9 Science Chapter Gravitation Notes Part I




If G Is Universal Gravitational Constant And G Is Acceleration Due



Gravity Of Earth Units Of Measurement Wiki Fandom




M 1l 3t 2 Are The Dimensions Of



Hal Archives Ouvertes Fr Hal Document




Universal Gravitational Constant And Gravitational Acceleration Of




The Search For Newton S Constant Physics Today Vol 67 No 7
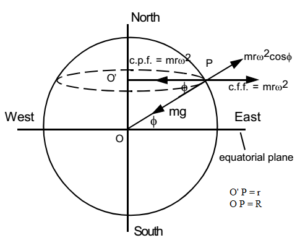



Variation In Acceleration Due To Gravity Due To Lattitude Height And Depth



Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation College Physics
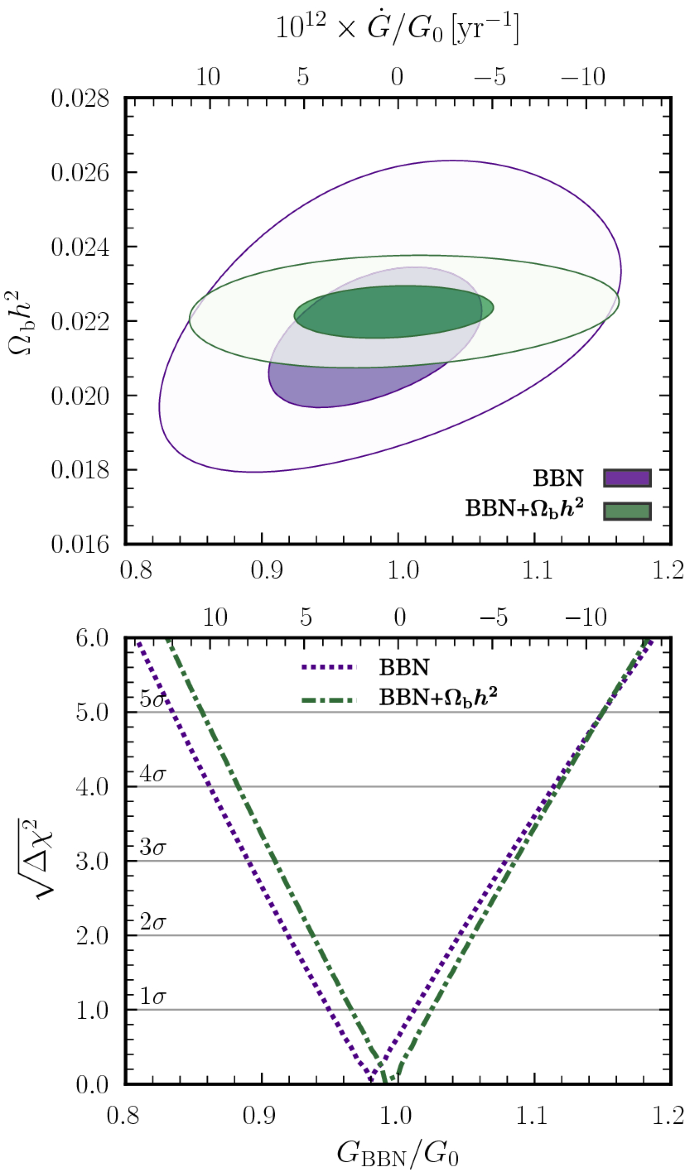



Improved n Constraints On The Variation Of The Gravitational Constant Springerlink




Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation Physics



Definition Of Gravitational Acceleration Chegg Com



What Is The Value Of Gravitational Constant G Quora




Big G Scientists Pin Down Elusive Gravitational Constant Live Science


コメント
コメントを投稿